Is the husband considered a close relative? Close relatives according to the "Family Code of the Russian Federation"
Each person clearly imagines his circle of close relatives, drawing himself a branchy family tree. Some people, on the contrary, withdraw from the family. This is a personal matter for any citizen, but everything is spelled out strictly and directly in the legislation. In regulations, various citizens fall under the definition of relatives - there is no general meaning. Further in the article, we consider who is a close relative under the law, and what inheritance rights such people have.
Concepts of legislative documents
The general definition of the term includes a group of people who are related by blood. These include parents and grandparents, children and grandchildren, siblings (even one common parent). This norm is prescribed in the Family Code of the Russian Federation. Not to be confused with family members. Thus, the latter is a group of citizens living together in the same premises for a certain period. Mother-in-law, son-in-law, mother-in-law, father-in-law, daughter-in-law, and even a common-law spouse - they are all considered family members, but are not legally related.
Attention! The article of the RF IC, Article 14, states that relatives are “relatives in a direct ascending and descending line (parents and children, grandparents and grandchildren, full and half (having a common father or mother) brothers and sisters."
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation supplements this category, in addition to those mentioned above, with legal husband/wife. The Criminal Procedure Code further expands the circle. Adopted children and adoptive parents are added to the list of close relatives.
Undoubtedly, there may be unique special cases when the determination of kinship occurs in the legal field, through the application of certain norms. It is worth considering that the interpretation of a concept in one regulatory area is not similar to another and is applied exclusively in specific cases. For example, defining a stepfather as a close relative in criminal law does not mean recognizing him as such in civil law.
Why is it important
By regulating various spheres of human life and society, regulations help in resolving various disputes. According to the law of the Russian Federation, close relatives are people who claim an inheritance without a written will. In the absence of this document, it is the children, grandchildren, parents, grandparents, sisters and brothers who are the primary heirs. Spouses, uncles, aunts, great-grandmothers, great-grandfathers, nephews go to other lines. 
For civil law, the definition of this concept is important when determining the tax rate on gifts and inheritance. Thus, property donated to such people is not subject to mandatory payment. For example, grandchildren do not have to pay tax when receiving a dacha as a gift from their grandmother. Duties are also established for inheritance and their amount depends on the degree of relationship.
In criminal law, there are provisions relating exclusively to immediate family, the circle of which is determined by the code. This is important for citizens who may refuse to testify in court against relatives, and who want to get a meeting with a prisoner. The law also prohibits the interrogation of minors without the presence of a parent or legal adoptive parent.
FAQ
The most common questions about close relatives are: does this include your wife/husband, stepfather, cousin, or spouse’s parents? Situations with inheritance are considered in more detail.
Husband or wife
The spouses are not related by blood to the testator, but according to the Family Code, husband and wife are family members. Between people in marriage, special relationships are formed, documented. This allows the testator's husband or wife to be in first line with the rest of the heirs in that group.
 A marriage certificate also provides privileges in the form of receiving half of the property in a divorce and the right to demand alimony for yourself and your children. However, there are also restrictions on marriage. This is consanguinity, the role of an adoptive parent or adopted child in a relationship, being in another marriage, or recognized incapacity.
A marriage certificate also provides privileges in the form of receiving half of the property in a divorce and the right to demand alimony for yourself and your children. However, there are also restrictions on marriage. This is consanguinity, the role of an adoptive parent or adopted child in a relationship, being in another marriage, or recognized incapacity.
Interesting! The husband and wife are not close relatives: according to the Family Code of the Russian Federation, they are relatives. That is, people who became related through marriage.
Stepfather or stepmother
Such people do not fall under this category in most situations, with the exception of the option of accepting the children of the wife/husband. Thus, by adopting a child from her husband’s first marriage, a woman becomes a legal close relative. In criminal law, a non-blood parent can act as a guardian and legal representative.
Cousins
Cousins, even if they are related by blood, are not considered closest relatives by law. The procedure for receiving an inheritance places this category of relatives in the third stage.
The parents of the spouses include: mother-in-law, father-in-law, mother-in-law, father-in-law. Even if they live together, they can only be family members and will never be considered otherwise. But at the same time, this category of relatives is the blood of their grandchildren. That is, children can claim the inheritance of their grandparents in the first place, unlike their son-in-law/daughter-in-law.
conclusions
Who are our closest people? Are these our spouses, relatives, friends? Often, life circumstances develop in such a way that blood relatives are indifferent to our fate, while the spouse with whom we have lived for decades becomes truly close, an inseparable part.
The life of each of us sets its own priorities. However, this is only the moral side of the issue, while the law provides for specific definitions in all areas of life. So, from the point of view of the law, are husband and wife relatives or not? Let's take a closer look.
Is the husband legally related to his wife or not?
For many ordinary people who do not delve into issues of legal subtleties, the answer to this question is obvious, since people who have a blood connection are usually considered relatives. And given the prohibition of Russian laws on concluding unions between close relatives, it follows that a husband and wife a priori cannot be relatives. However, in the codes of the Russian Federation, the answers to this pressing question vary.
Close kinship and family law
So, kinship is a special blood connection that arises between people.
There are 6 degrees of consanguinity (the number of births between relatives is called the degree):
- parents and children, brothers and sisters;
- grandparents and their grandchildren;
- great-grandparents and their great-grandchildren;
- cousins, grandparents, and great-nephews;
- great aunts and uncles, as well as nephews;
- second cousins.
At the same time, the concepts of close and distant kinship are distinguished. Close relatives are considered to be ancestors and descendants along horizontal and vertical lines, while all others are distant.
 Close relationship:
Close relationship:
- grandmother grandfather;
- mother father;
- son daughter;
- grandson, granddaughter.
- full brothers, sisters;
- not full brothers, sisters (having only one parent in common).
There is a widespread belief that the concept of close kinship is based on the principle of common genes or, in other words, common blood. However, persons of direct intergenerational kinship (great-grandparents, great-grandfathers), who undoubtedly have common genes, are nevertheless not considered close relatives.
The fact is that only the first two degrees are considered close kinship, that is, relatives with no more than two births between them (parents - children, parents - children - grandchildren). On the other hand, adoptive parents and adopted children who have no blood relationship are recognized as close relatives.
This is primarily due to the fact that, according to existing laws, adoption (or adoption) is actually equivalent to the birth of one’s own child in the family.
Thus, adoptive parents are recognized as full-fledged parents. It should be noted that we are talking specifically about adoption; the agreed formalities have nothing to do with the adoptive family (guardianship).
Family law is fully guided by the above principles and only the first two degrees of kinship are recognized as close relatives.
Thus, according to the RF IC, spouses are not recognized as relatives. However, the RF IC introduces such a concept as “family members,” which includes spouses.
Family members also have a number of advantages:
- (in the absence of a will);
- spouses have equal rights to everything.
Criminal Code
In matters of kinship, the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation differs significantly from the RF IC and recognizes spouses as close relatives. This state of affairs is not accidental.
 In accordance with the Code of Criminal Procedure, close relatives:
In accordance with the Code of Criminal Procedure, close relatives:
- have the right not to testify against each other. In many criminal cases, the evidence base is built precisely on the testimony of witnesses, so the opportunity not to testify is a kind of immunity from pressure from prosecutors;
- do not bear criminal liability in case of failure to report a crime being prepared or committed by his close relative.
Let's look at these issues in more detail and consider the following situations:

- giving false testimony (perjury);
- complicity in a crime;
- touching the crime.
Close relatives are most interested in the future fate of the accused.
This is especially true for spouses, who, among other things, may have common minor children, property, and debt obligations (mortgage,). Not surprisingly, there is a high likelihood of them giving false testimony in order to mislead the authorities about the guilt of the suspect.
However, a false witness can be exposed, prosecuted and criminally punished. Therefore, in order to avoid such a situation, close relatives are given the right not to testify at all. Every citizen is considered innocent until proven otherwise.
 Witnesses who are close relatives of the accused are under enormous stress, they are confused, disoriented, and emotionally depressed.
Witnesses who are close relatives of the accused are under enormous stress, they are confused, disoriented, and emotionally depressed.
Often, under additional pressure from authorities, relatives provide information that can harm themselves, turning from a witness into an accomplice. In such cases, it is more advisable not to give evidence at all or to give it in the presence of a lawyer.
Touching a crime differs from the concept of direct complicity, but touches on a very sensitive point. The concept of “touching a crime” can be characterized by a situation in which a citizen, aware of an impending crime, does not report it to the authorities.
Who knows you better than others? Who do you spend almost every day with? Who are you constantly in sight of? The answer is obvious - these are the closest ones, this is the family, husbands and wives, sons and daughters. They should have suspected something was wrong, noticed something suspicious and, accordingly, reported what was happening to the authorized body.
Guided by this logic, all close relatives of each accused who did not report his planned crime become involved in the crime and are subject to punishment. Obviously, such logic is irrational.
If a criminal case has been brought against your close relative, first consult with a lawyer about the need and advisability of testifying.
Civil Code
 The Civil Code of the Russian Federation operates with the concept of “close relationship”, but does not provide a specific list of persons who can be classified as close relatives.
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation operates with the concept of “close relationship”, but does not provide a specific list of persons who can be classified as close relatives.
In matters of family legislation, the Civil Code of the Russian Federation is directly related to the Family Code. The concepts in the Civil Code and the RF IC are closely intertwined, thus, according to the RF IC, in matters of settling civil relations, husband and wife are not relatives to each other, but family members.
Housing Code
 The Housing Code of the Russian Federation provides for the concept of “family members,” which include: spouses, as well as children and parents of the owner of the property, but the concept of “close relationship” is completely absent.
The Housing Code of the Russian Federation provides for the concept of “family members,” which include: spouses, as well as children and parents of the owner of the property, but the concept of “close relationship” is completely absent.
All rights and obligations provided for by the RF Housing Code apply to family members. At the same time, any citizen registered by the owner can actually become a member of the family.
Therefore, in housing matters, the presence of consanguinity is not important.
Labor Code
 The Labor Code of the Russian Federation also does not provide for the concept of “close relative,” redirecting us again to the RF IC.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation also does not provide for the concept of “close relative,” redirecting us again to the RF IC.
The definition of close relationship for the Labor Code is most sensitive in matters of providing vacation days at one’s own expense in the event of the loss of a close relative.
Guided by the definition given by the RF IC, in the event of the death of a spouse, the employer is not obliged to provide the employee with leave at his own expense, since the spouses are not close relatives.
From a moral point of view, this is outrageous. Unfortunately, there are many similar cases in our legislative framework.
Tax law
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation uses two definitions - a close relative and a family member (or in-law). At the same time, considering both definitions, tax legislation again redirects us to the Family Code, according to which a husband and wife are members of each other’s family.
Spouses have the same privileges as blood relatives in the following tax cases:
- . Profit received as a result of a gift between spouses is not subject to tax. However, there is one caveat - the marriage must be officially registered. A man and woman who live together without registering their relationship in the registry office are not officially considered spouses. In addition, only gifts from current spouses are not subject to tax; this privilege does not apply to former spouses;
- . At the time of entry into inheritance rights, the spouse pays only half of the prescribed state duty.
As you can see, in matters of close kinship, even the letter of the law does not have a single definition. Therefore, if a situation arises that requires specificity and clarity in this matter, it is better to seek the help of qualified lawyers.
" style="margin-top: 1px; margin-right: 1px; margin-bottom: 1px; margin-left: 1px; " id="the_adid1012">
Close ones are considered to be those people with whom you constantly live in the same living space and spend the maximum amount of time. And many do not take into account real blood relationships. But the law looks at this concept a little differently.
In Russian legislation, kinship is used when various legal relationships arise between individuals. persons. For example, division of property, inheritance or registration of a deed of gift.
Special relationships arise between close relatives, formed by certain generally accepted moral norms. The very fact of consanguinity does not give the right to violate human rights (even of a minor). This is why a mother and father who do not care for their children may be deprived of their rights (but not their responsibilities).
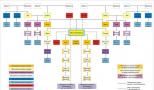
Most often, such kinship is used in family law. In Art. 14 of the Family Code provides a definition of this concept. So, close relatives are a person’s relatives in a descending or ascending line:
- mother father;
- children;
- grandmothers, grandfathers;
- brothers, sisters.
It is important to take into account that adoption is equivalent to close kinship. Therefore, the adoptive parent and the child are related to each other in the same way as relatives. As for siblings, they can have both parents in common or just one, it doesn't matter.
Housing law
The term “close relatives” is not used in housing law. Most often in regulations you can find the concept “members of the same family.” These include not only immediate relatives, but also spouses, nephews, uncles, aunts, and other family members living together.
Labor law
According to the Labor Code, the concept of close relationship is quite vague and is used extremely rarely. For example, employers can independently determine the degree of relationship of their subordinates when hiring. Thus, many companies prohibit hiring members of the same family. But in this case they may include both spouses or parents (children), as well as distant relatives (cousins or great-nephews).
Tax law
In tax legislation, the concept of relationship is used only when carrying out certain procedures. For example, we may be talking about paying taxes when receiving property by inheritance or gift. Under these circumstances, they are considered not only the mother, father, children or grandparents, but also the husband and wife.
Administrative legislation
The norms of administrative law establish that the concept of “close relatives” is used when it is necessary to testify in a case of administrative offenses (Article 25.6 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
The note to this article contains a list of persons who cannot act as witnesses and against whom it is possible not to testify. These include all blood members of one family (children, parents, etc.). But husband and wife are not included in this list.
Criminal law
Close kinship also plays a significant role in criminal law. Thus, Article 5 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation contains a list of persons who belong to close relatives within the framework of criminal proceedings. In addition to blood (adopted) family members, they include spouses.
In inheritance matters
If we talk about inheritance, then everything is not very clear when it concerns spouses. In other cases, the norms of family law are used (Chapter 63 of the RF IC), which determine the degree of relationship of each of the heirs.
In law
When receiving movable or immovable property without a will, a certain order of heirs is used. For example, the direct heir is the spouse of the deceased, then his children, parents, brothers, sisters and so on. There are seven such queues in total, and the last applicants are stepfather, stepmother, stepdaughter, stepson.
By will
In the case where a will is used, kinship plays virtually no role. The owner of property can bequeath it both to members of his family and to an outside person or even an organization. But if the testator indicated only close relatives as heirs, then by law his spouse is not included in their number. Therefore, the child, parents, brothers, sisters will receive the property.
Who is not closely related
The standard list of persons who are close relatives contains Art. 14 RF IC. In most cases, it remains unchanged, except in situations where spouses are equated with them.
If we are talking about family members who may be blood relatives, but no more, then these include:
- uncles, aunts;
- nephews, nieces;
- stepfather, stepmother, stepson, stepdaughter;
- mother-in-law, father-in-law, brother-in-law.
For example, even a nephew is not considered a close relative by law. When receiving any apartment or other property under a gift, he will have to pay tax.
Are they close relatives?
There are a number of persons who can be members of the same family, but cannot be closely related to each other.
Spouses by law
It seems that there is no one closer than husband and wife, but from a legal point of view this is not entirely true. A husband and wife cannot be blood relatives, since the nature of the relationship between them is completely different. The law defines them as inherent relations. This also applies to father-in-law, mother-in-law, and also to son-in-law and father-in-law.
Former spouses
If we say that spouses can only partially be relatives to each other (or simply members of the same family), then this cannot be said about former spouses. When a marriage is dissolved, they cease to be part of the same family and all their relationships are terminated.
Rights and obligations arising from the concept of close relationship
It is not for nothing that this legal term limits the circle of persons who have a real blood relationship. They may not live together or even see each other, but they should be aware of their rights and responsibilities.
Responsibilities include:
- education (maintenance) of young children;
- maintenance of disabled parents;
- responsibilities that arise when registering a marriage.
There are certain rights:
- the right not to testify against a close relative during administrative or criminal proceedings;
- right of inheritance by law;
- the right to receive alimony payments for children (or former spouses);
- right to tax rebate or other benefits.
An individual’s belonging to a particular family gives rise to rights and responsibilities. Their list is much wider than it might seem at first glance. In addition, the alienation of rights and obligations in this case is carried out only for special reasons (only partially). For example, when a father or mother is deprived of parental rights.
The concept of close relatives is often used in the current life of every person. In everyday life, such relatives are understood to be blood and step-relatives of the same or immediate generations.
The legislative definition is broader and more complex; it is reflected in the provisions of the Family Code and other legislative acts and is important in the exercise of inheritance rights, primarily when called upon by law.
The Family Code is an act of lawmaking that regulates relations between relatives. Determination of kinship is carried out in accordance with Art. 14 SK.
Blood ties can be expressed in the form of ascending and descending kinship, which implies kinship:
- one generation (brother/sister);
- neighboring generations (parents/child);
- through a generation (grandfather, grandmother/grandchildren).
Brother, sister
A citizen's relationship with a brother or sister can be either. Full blood ties of these relatives are determined by the presence of both common parents. In the event that one of the parents is common, the brother is a close relative, as is the sister.
Husband wife
Citizens who have legally registered their relationship are recognized by current legislation as a family. In fact, there is not and cannot be a close relationship between spouses, because marriages are between relatives.
Marriage must be understood as a union, the consolidation of which is carried out by an agreement establishing the range of mutual rights and obligations of the spouses. Despite the fact that there is no blood relationship between the spouses, the surviving spouse is given the right of inheritance. This right ends upon divorce.
In fact, it is impossible to determine the degree of relationship between the spouses, but the law establishes their legal status, according to which the spouses are close relatives.
Grandmother grandfather
The blood relationship must connect the grandmother or grandfather with one of the parents, i.e. father or mother of a grandson or granddaughter. This relationship is considered close and is expressed as a connection through a generation.
Nephews
The question of whether a nephew is a close relative may be important in family and inheritance relations.
Despite the fact that nephews are children of sisters and brothers (consanguineous or step-brothers), they do not have the rights of close blood relatives that belong to such persons.
Is the mother-in-law a close relative?
Legislatively, the relationship between mother-in-law and son-in-law, as well as the relationship between mother-in-law and daughter-in-law, are defined as property. There is a family connection between a son-in-law and father-in-law/mother-in-law, and between a daughter-in-law and father-in-law/mother-in-law.
Despite the fact that there is no close relationship between these individuals, they can be considered one family.
How can an heir confirm his relationship?
Confirmation of relationship between close relatives, necessary for the purpose of receiving an inheritance, can be carried out by providing supporting documents, which include:
Where should I go?
 You can obtain missing documents on kinship from the authorities, as well as from... If it is not possible to obtain documents on kinship, discrepancies in the information in them, or in other cases, it is necessary to confirm the kinship.
You can obtain missing documents on kinship from the authorities, as well as from... If it is not possible to obtain documents on kinship, discrepancies in the information in them, or in other cases, it is necessary to confirm the kinship.
In view of the fact that the period for accepting an inheritance is, it is necessary to begin legal proceedings as quickly as possible.
Required documents
The birth certificate of both can be used as documents confirming the relationship between a sister and brother. Adoption documents will have equal force.
Additionally, you can use the parents’ passports, which contain a note about the children.
The birth certificate will confirm the presence of family ties with the parents. You can prove your blood relationship with your grandparents by providing your own birth certificate and a similar document issued in the name of the parent. In this situation, documentation may be required confirming the fact of changing the surname upon marriage.
Drawing up an application
The first step to starting a trial is filing a statement of claim, which must reflect:
- name of the court authorized to consider the case;
- data of the plaintiff, defendant and interested parties;
- description of all circumstances and information known about relatives;
- justification of the need to confirm kinship;
- the party's demand with reference to legislative norms.
The claim must be supported by available documentation available to the plaintiff, on the basis of which the court can come to a conclusion about the presence or absence of kinship.
In order to avoid leaving the claim without progress, the plaintiff must pay in advance and attach a receipt for its payment to the claim sent to the court.
To substantiate the claims reflected in the claim, certain documentary materials must be attached to the document, including:
- certificates confirming birth, death, marriage, divorce, change of name;
- photos and videos;
- correspondence;
- certificates received at the place of residence;
- medical reports on genetic relationship;
- profiles, biographies, etc.
At the same time, the court can be provided with a certificate obtained from the person, indicating that the latter received a statement from the plaintiff about his intention to accept the inheritance.
Witness testimony may be important. Other relatives, acquaintances and people close to the family can take part as witnesses in the process.
On its own initiative or based on requests from the parties to the case, the court has the right to request other evidence. They can be obtained from:
- Civil registry offices;
- archives;
- educational and medical institutions;
- place of employment.
Consultant answers to questions from our readers
How to prove relationship?
Our family has a plot at the Lublin cemetery. My uncle has been put in charge of it. At the moment, the following are buried there: the parents of my uncle and my mother, who were my grandparents, my grandmother’s sister and her husband.
Due to the fact that my uncle is elderly, he had a desire to place responsibility on me. When preparing the relevant documents, we were required to provide evidence of my relationship with the buried persons. Unfortunately, no documents about the relationship have been preserved.
In the family archives we found only a marriage certificate between grandparents. How can I prove my relationship? On the basis of what document am I obliged to prove it in relation to the buried? Will there be enough documents confirming your relationship with your uncle?
If it is necessary to re-register a burial place, the responsible person, i.e. Your uncle and you, as the new person in charge, must write an application for re-registration.
Such an application must be accompanied by documents indicating your relationship with the buried. In the absence of such documents, the relationship will need to be proven in court.
Can relationship be proven?
Can't prove relationship. This must be done in order to receive an inheritance based on a will. The cause of the problem was a discrepancy between the entry in the birth certificate issued by the registry office and the register of the fact of my birth.
Today, I applied to the registry office for a duplicate due to the document being unusable (the part containing the entry number was torn off).
You can prove the existence of a relationship without a birth certificate only in court, with the presence of other evidence confirming your relationship, for example, DNA examination.